Print positing flashcards Easy Notecards
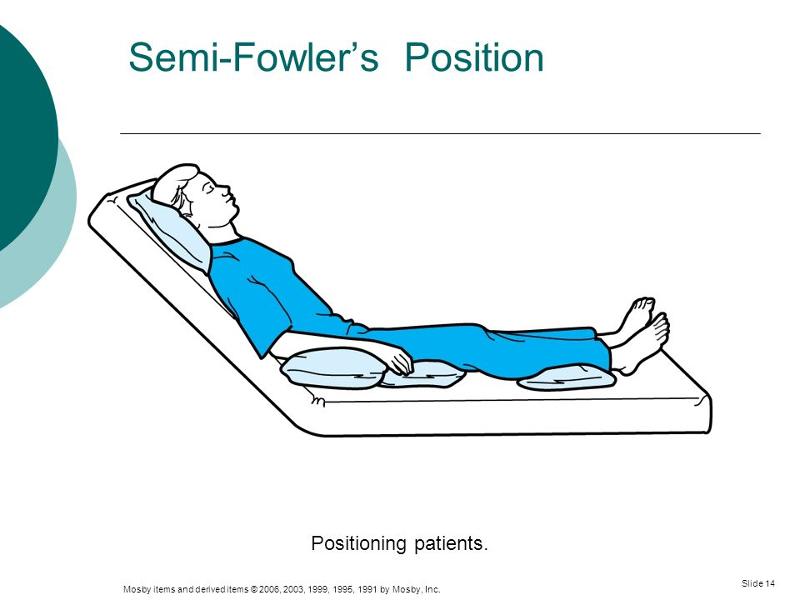
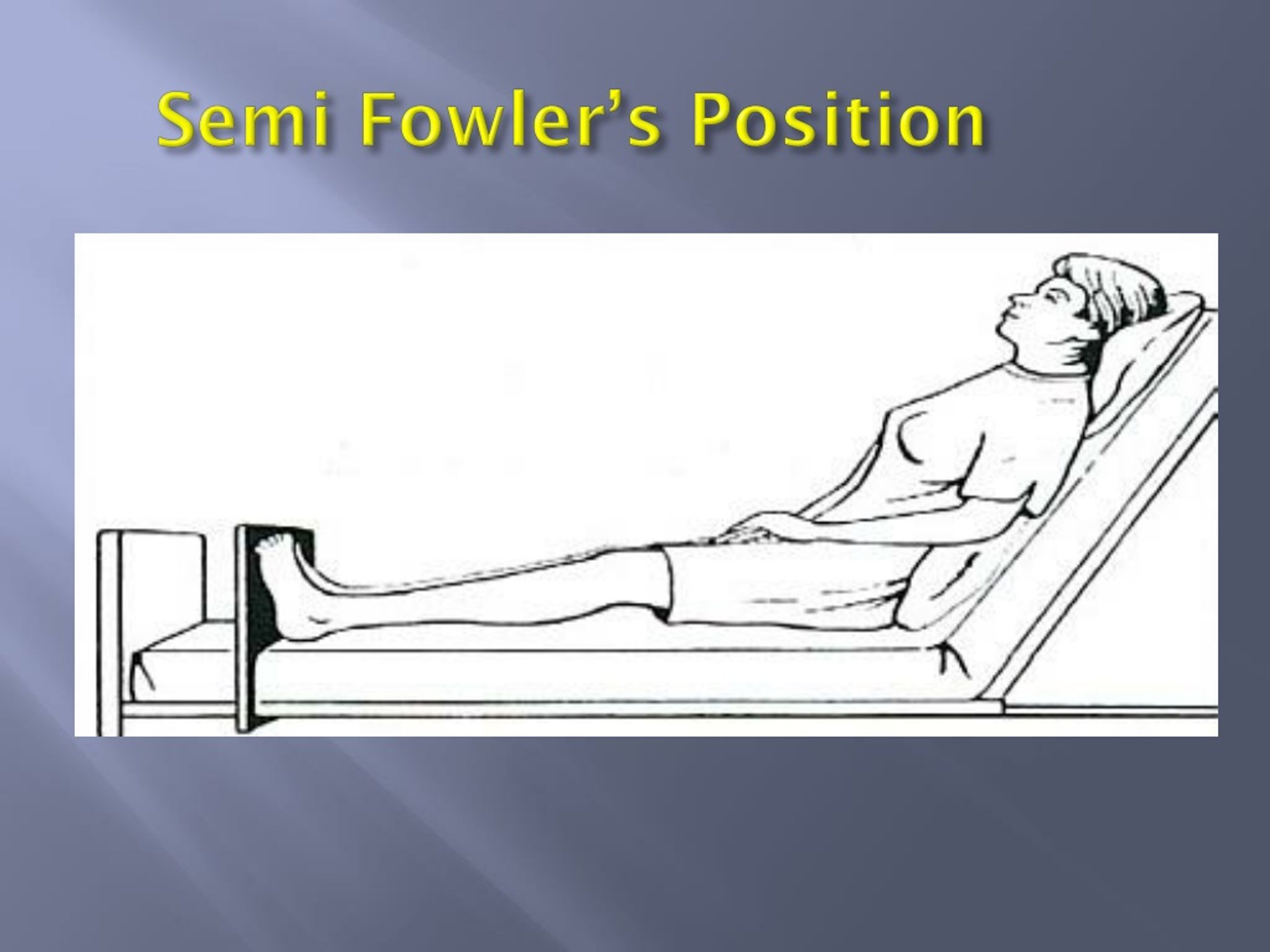
A semi-Fowler's position is similar to the standard Fowler's position, however, the head and back rest at a lower angle. The bed is typically inclined at an angle of 15 to 45 degrees, although 30 degrees is most frequently used. This position is implemented for a number of medical reasons including:
Fowler’s position, uses for Fowler’s position
Semi-Fowler's position. A person is in the semi-Fowler's position if they lie supine on a bed that is inclined at an angle of 30 to 45 degrees. This position is often applicable for patients who have heart problems, respiratory disorders or neurological problems. Related Posts.
Fowler’s position, uses for Fowler’s position
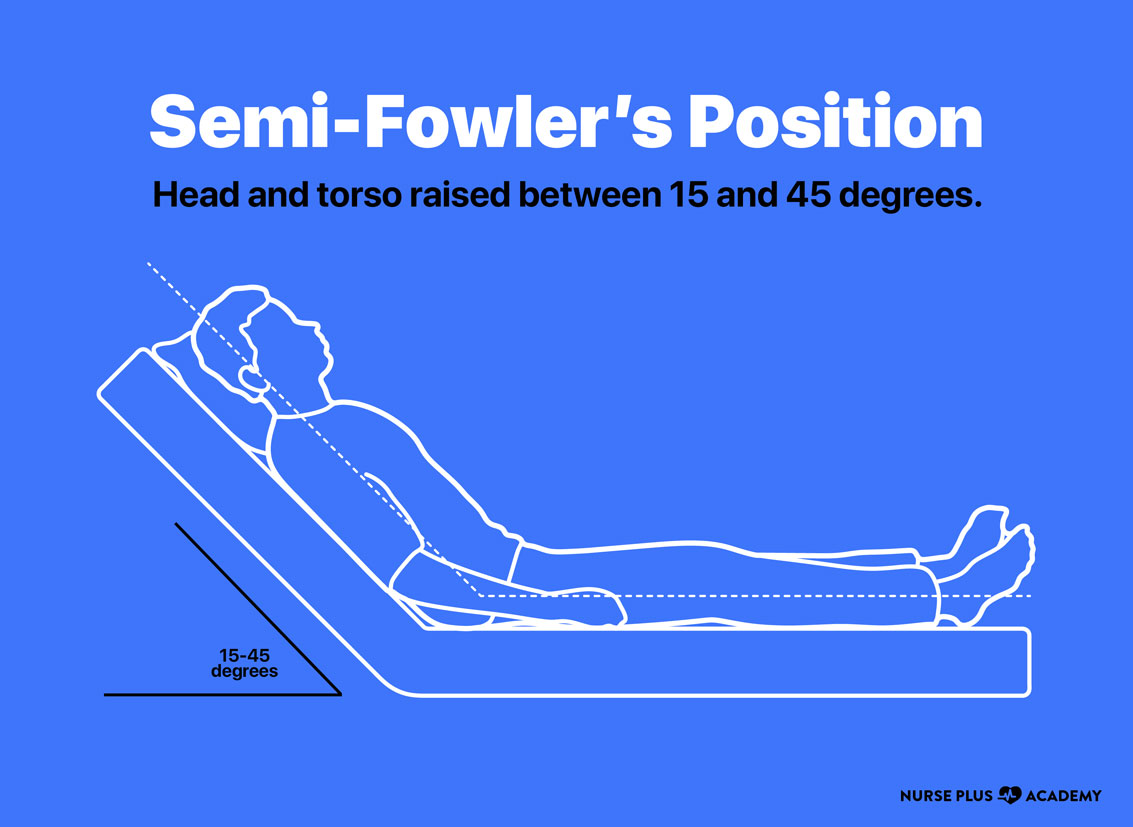
The Semi Fowler Position is when a patient is placed on their back with their head and trunk lifted to between 15 and 45 degrees, usually in a hospital or nursing home, however, 30 degrees is the most common bed angle. The elevation is lower than in Fowler's position, and it might involve raising the bed's foot to the level of the knee so that.

Flashcards Positions Semi fowlers position null StudyBlue
The Semi-Fowler's position is often used for purposes similar to those of the regular Fowler's position, including. feeding; lung expansion; cardiac or respiratory conditions; for patients with a nasogastric tube; The Semi-Fowler's position is also uniquely preferred during childbirth because it improves the comfort of the mother. Related Terms
SemiFowler's position Nurse Plus
The semi-Fowler's position facilitates breathing of patients and may be one of the explanations for the higher comfort VAS scores in the semi-Fowler's position group. In the semi-Fowler's position, changes in systemic circulatory blood volume might cause transient hypotension. Therefore, we paid careful attention to hemodynamic changes.

Basics of Nursing Practices and Interventions Faculty of Medicine
Patient Positioning: Complete Guide and Cheat Sheet for Nurses. Updated on September 3, 2023. By Matt Vera BSN, R.N. In this guide for patient positioning, learn about the common bed positions such as Fowler's, dorsal recumbent, supine, prone, lateral, lithotomy, Sims', Trendelenburg's, and other surgical positions commonly used.
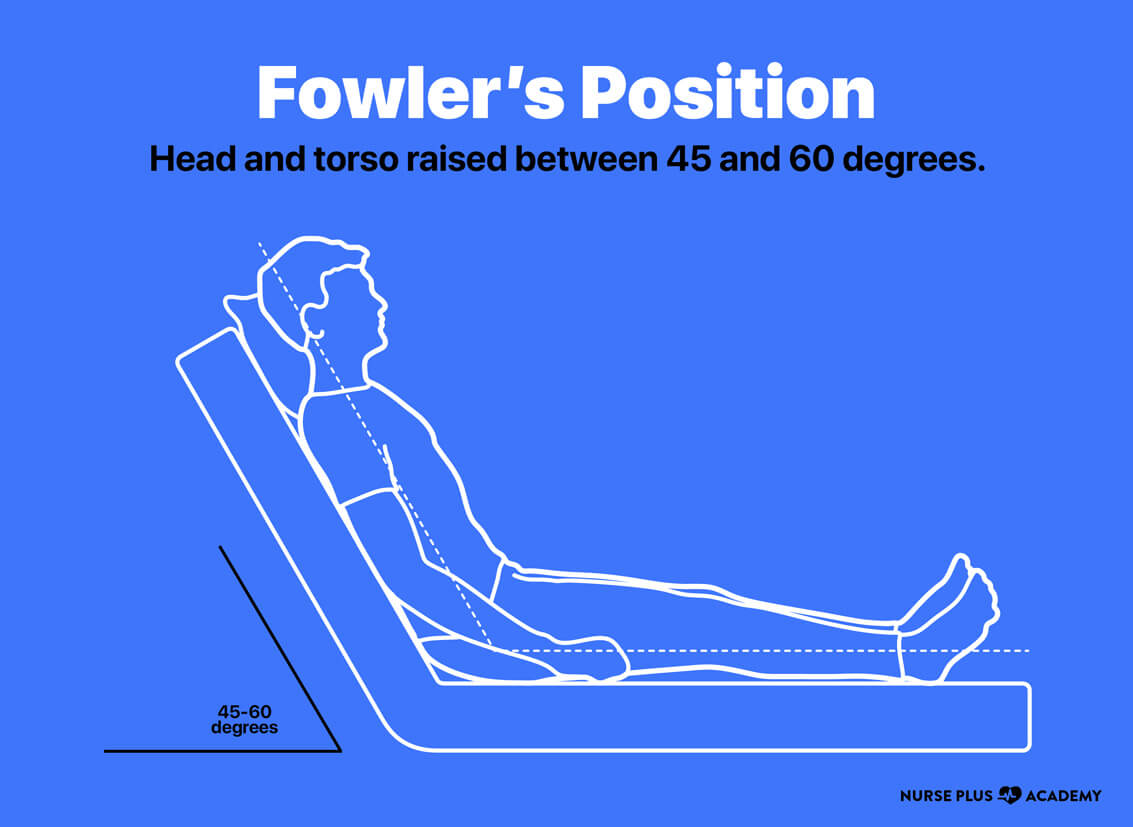
Fowler's position Nurse Plus
Semi-Fowler's Position. An official website of the United States government. Here's how you know. The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure..

Positioning 1
The Semi-Fowler's position is a position in which a patient, typically in a hospital or nursing home in positioned on their back with the head and trunk raised to between 15 and 45 degrees, although 30 degrees is the most frequently used bed angle..
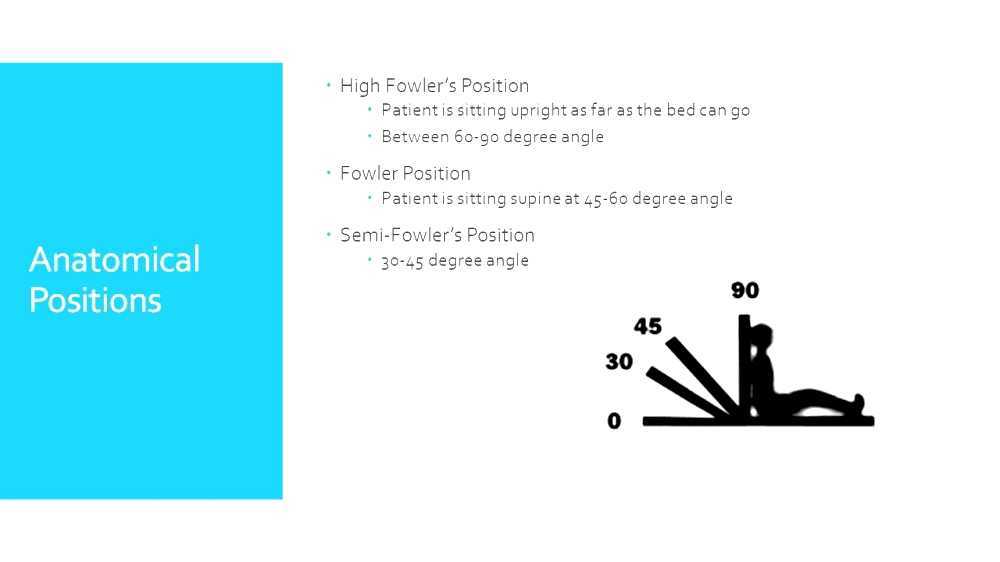
Fowler's position
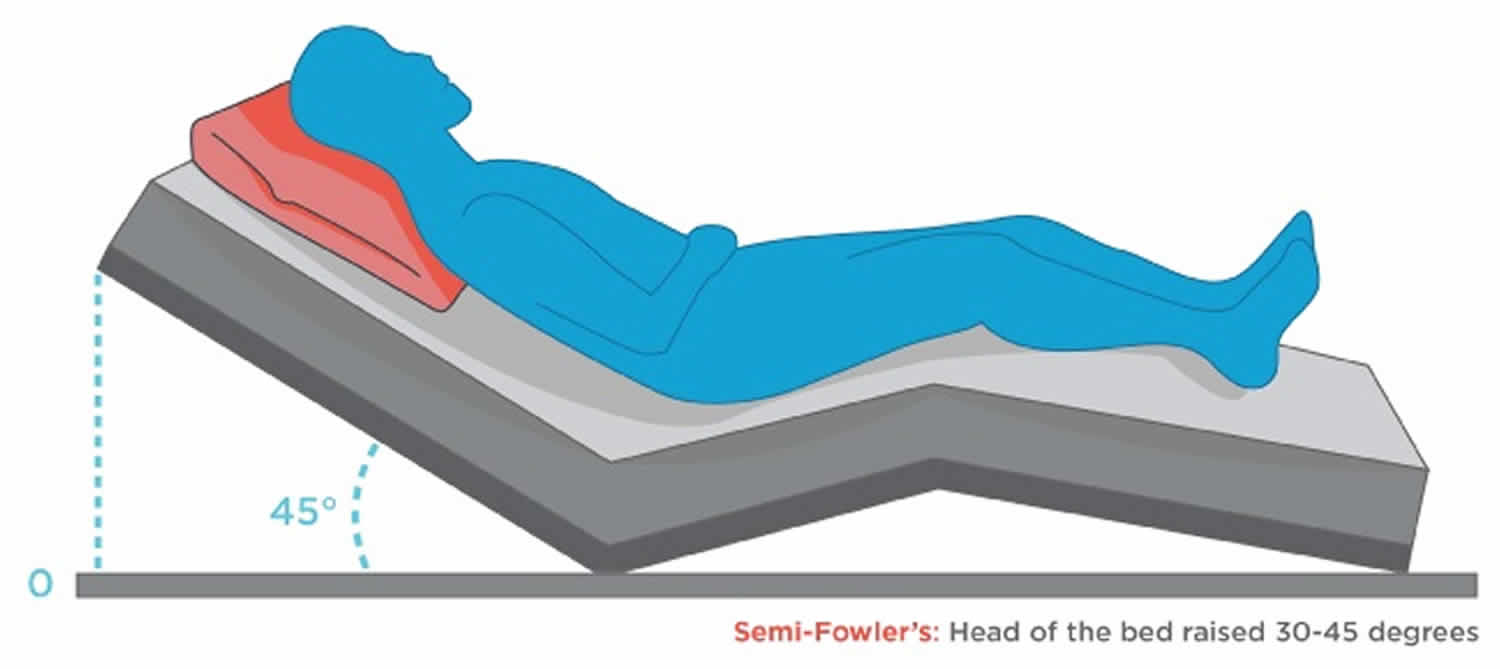
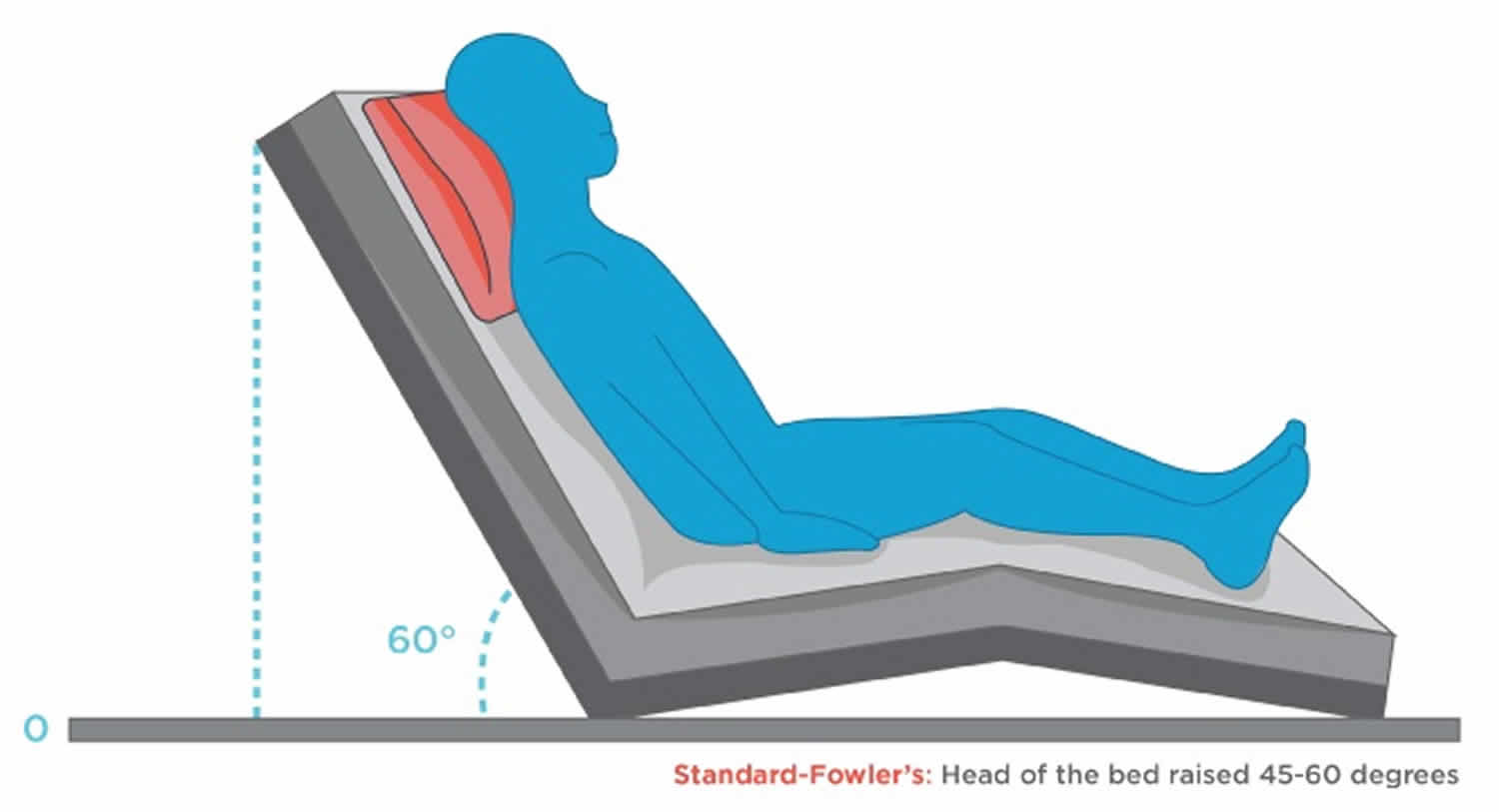
Semi Fowler's position: The head of the bed is raised at 30 to 45 degrees. The legs may be straight or slightly bent. This position is often used for respiratory treatments, recovery from abdominal surgery, and labor and delivery. Standard Fowler's position: The head of the bed is raised at 45 to 60 degrees. The legs may be straight or.

Figure 39. SemiFowler's position. Nursing Care of the Surgical Patient
The bed angle in standard Fowler is greater, with the head of the bed elevated at 45-60 degrees, while in a semi-Fowler position, the head of the bed is elevated 30-45 degrees. The standard Fowler position is commonly used for head, shoulder, and chest surgeries as well as for respiratory distress syndrome as the position facilitates breathing.
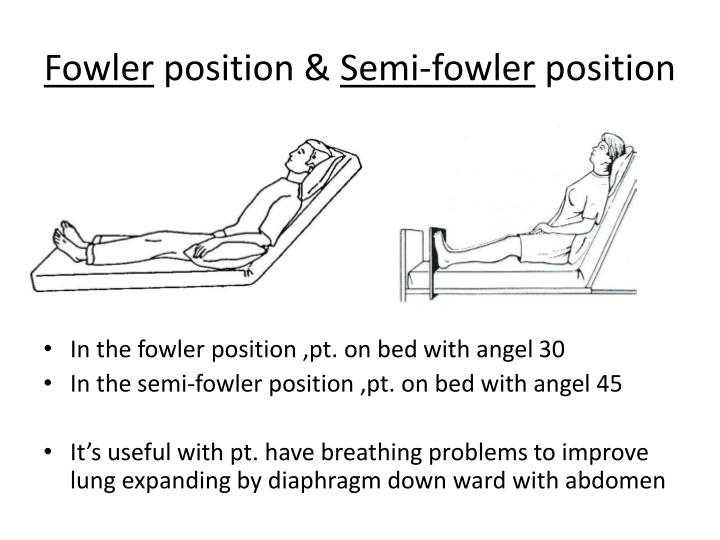
PPT Client’s positions PowerPoint Presentation ID2561698
The Semi-Fowler's position is a position in which a patient, usually in a hospital or nursing home, is lying on their back with the head and torso raised between 15 and 45 degrees. The most frequently used bed angle for this patient position is 30 degrees. The elevation angle is smaller than that of the Fowler's position, and may include raising the foot of the bed at the knee to bend the legs.
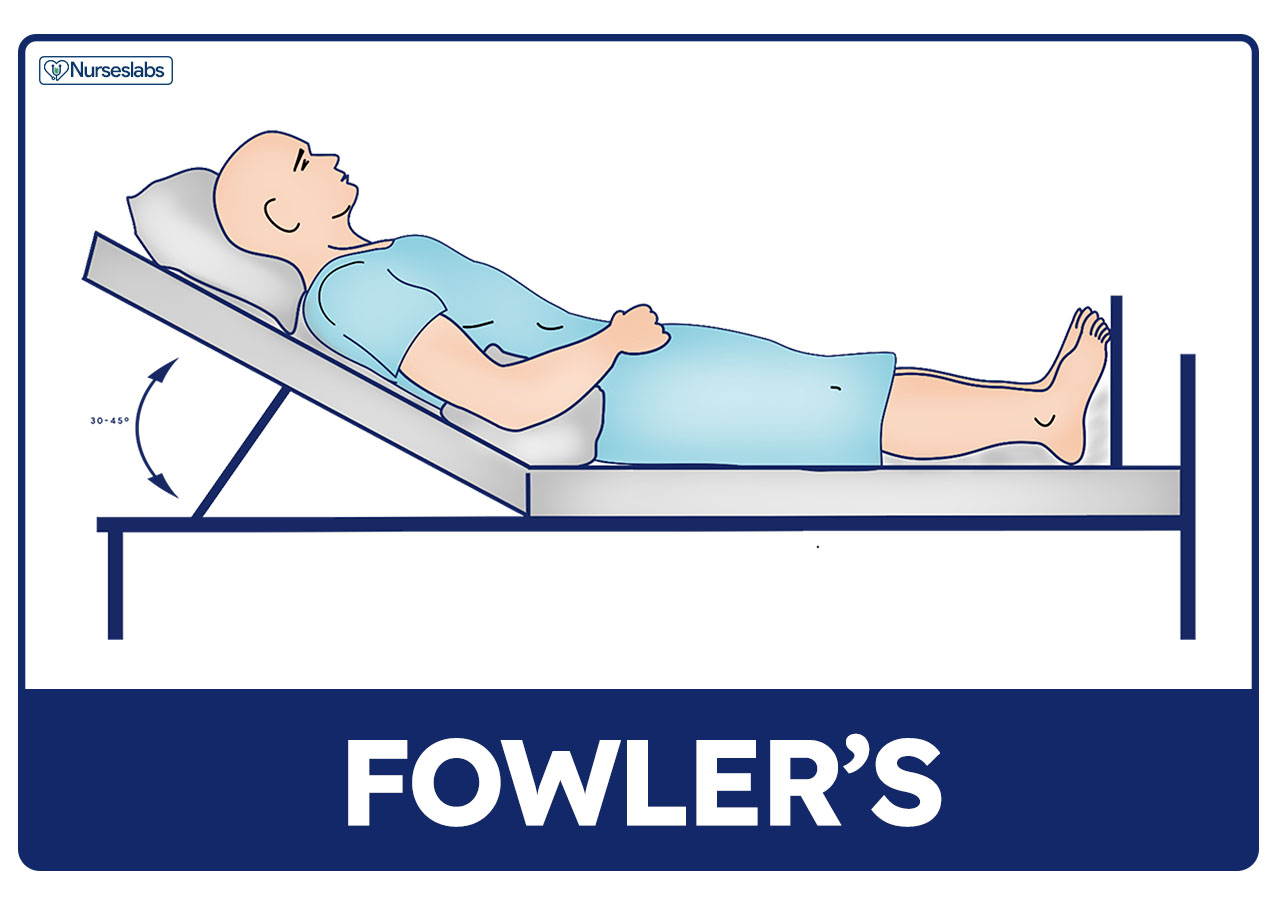
Low Fowlers Position
Material and methods. One hundred and six patients (mean age: 43 ±12 years) undergoing gynaecologic laparoscopic surgery (LS) were included. The patients were divided into three groups: group 1 consisted of patients receiving PRM in the neutral position, group 2 comprised patients receiving PRM in the semi-Fowler position, and patients in the control group received neither PRM nor additional.

Pin on Humans
In the standard Fowler position, the head of the bed is elevated between 45-60 degrees, and this position is commonly used for head, shoulder, and chest surgeries as well as for respiratory distress syndrome because it facilitates breathing. In the semi-Fowler position, the bed angle is between 30-45 degrees, and this positioning is recommended.
PPT Mobility and Immobility chapter 47 PowerPoint Presentation, free
The Semi-Fowler's position is an inclined medical position where the patient is on their back at a bed angle between 30°-45°. Used for similar Fowler's position purposes that include lung expansion and feeding, the Semi-Fowler's position is uniquely preferred during childbirth to improve the comfort of the mother. The foot of the bed.

Figure 1 from Effects of trunk posture in Fowler's position on
Fowler's Position. Fowler's position, also known as sitting position, is typically used for neurosurgery and shoulder surgeries. The beach chair position is often used for nasal surgeries, abdominoplasty, and breast reduction surgeries. When positioning a patient in Fowler's position, the surgical staff should minimize the degree of the patient's head elevation as much as possible and always.

How to Pull a Chest Tube (with Pictures) wikiHow
Appropriate patient position can facilitate proper physiologic function during pathophysiologic processes and also facilitate access to certain anatomical locations during surgical procedures. Multiple factors should be considered when choosing the patient's position. These factors include patient age, weight, and size as well as past medical history, including respiratory or circulatory.